The Essential Guide: How to Choose the Right Insulation for Your Home
Choosing the right insulation for your home is key to maintaining a comfortable, energy-efficient living space. Our guide on “how to choose the right insulation for your home” demystifies the process, helping you assess your insulation needs based on climate, home design, and R-values without the jargon. Discover practical advice to make an informed selection that will keep your energy bills low and comfort high.
Key Takeaways
-
R-values are critical for assessing insulation effectiveness, with higher R-values indicating better thermal resistance, and must be considered alongside factors like material, thickness, and installation quality.
-
The choice of insulation should be based on an analysis of the home’s existing insulation, local climate, and specific design, with different materials and strategies suited for various parts of the house to maximize energy efficiency.
-
Installation technique is crucial for insulation performance; proper sealing, coverage, and professional expertise can significantly influence the long-term benefits and cost savings of insulation upgrades.
Deciphering R-Values and Thermal Resistance
R-values are the guardians of your home’s thermal fortress, a key measure determining how well your insulation can fend off unwanted heat transfer. This comprehensive guide will navigate through the complex world of R-values, explain the factors affecting thermal resistance, and equip you with the knowledge to evaluate insulation materials effectively.
With this power, you’ll be well-prepared to choose the right insulation that stands as a bulwark against the elements.
Understanding R-Values
The R-value is more than a mere number—it serves as a helpful tool in your pursuit of thermal comfort. With higher R-values signaling a material’s superior ability to resist the siege of heat flow, you’ll want to amass the highest R-value you can afford for your walls, ensuring a stronghold against energy inefficiency.
Remember, doubling the thickness of your insulation doubles the R-value, reinforcing your home’s defense against the seasons.
Factors Affecting Thermal Resistance
However, insulation thickness isn’t the only factor in thermal resistance—the material’s inherent thermal conductivity also has a significant impact. To preserve the desired R-value, the installation must be impeccable, avoiding any compression that could weaken your thermal barrier.
Comparing Insulation R-Values
When comparing insulation materials, remember that the highest R-value is not always the conqueror. The style of your building and the environment it resides in will dictate the level of heat resistance required.
For instance, insulating a suspended floor with in-slab heating necessitates an insulation R value of not less than 1.0—a strategic decision for your home’s thermal efficiency.
Identifying Your Insulation Needs

Before you can reinforce your home, you need to understand your current situation. Insulation acts as a barrier to heat flow, essential for year-round comfort. By assessing your current insulation, considering your local climate, and taking into account your home’s unique design, you’ll be able to devise a tailored insulation strategy that will optimize energy efficiency and safeguard your domestic domain.
Analyzing Current Insulation
Indications of insulation flaws can be found if you know what to look for. Temperature inconsistencies, high energy costs, and chilling drafts are telltale indicators that your home’s defenses are compromised. By examining walls and outlets or even inspecting a small sample of material, you can assess the strength of your current insulation and plan reinforcements where needed.
Climate Considerations
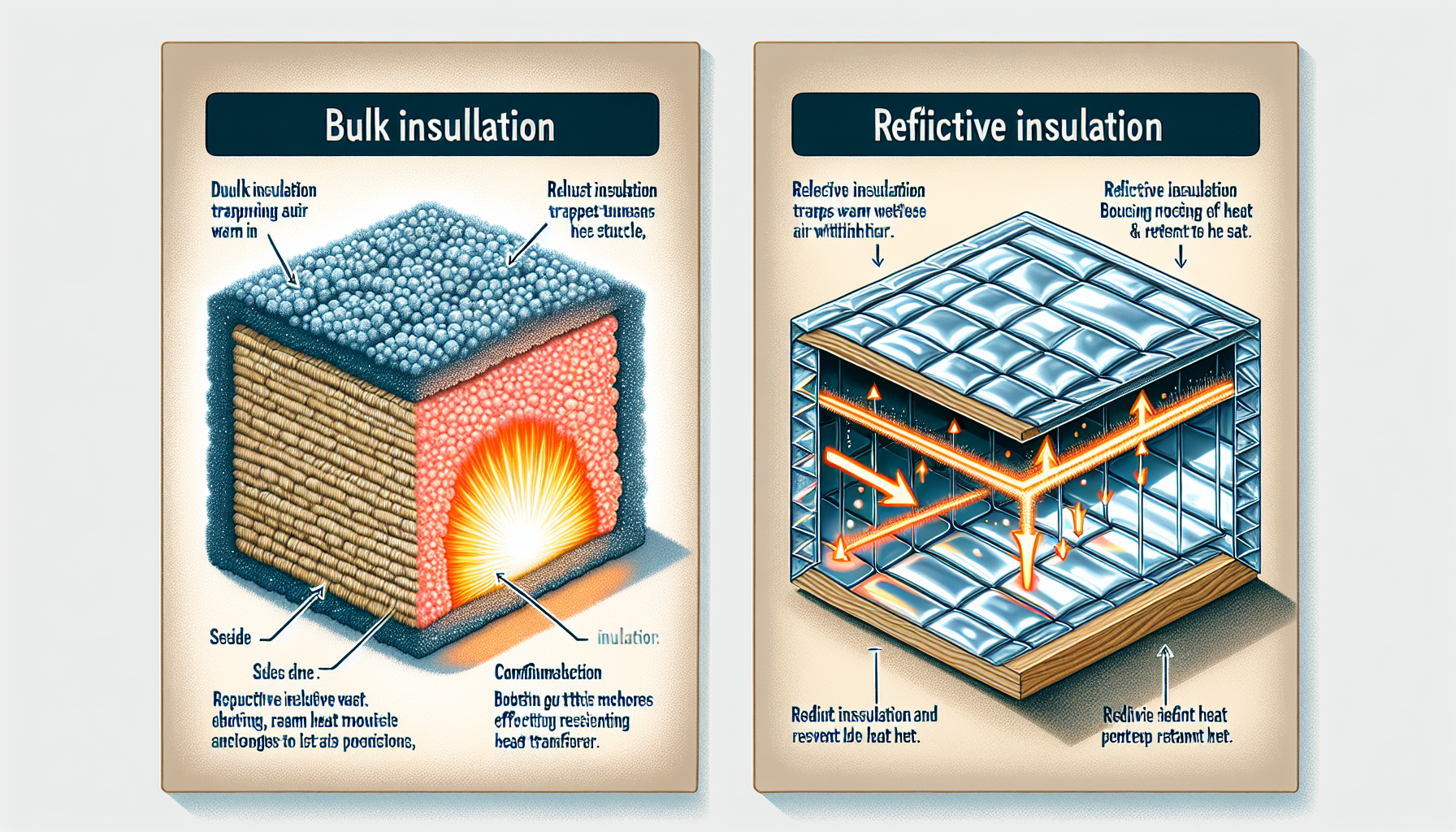
The climate you dwell in will dictate the type of insulation your home requires—like choosing the right armor for battle. In warmer climates, reflective insulation repels the heat with its shiny armor, while in cooler realms, bulk insulation traps air to retain warmth.
Home Design and Insulation Strategy
The design of your home, including its layout and orientation towards the sun, significantly influences your insulation strategy. By considering these design elements, you can effectively integrate insulation into your home’s defenses, ensuring no energy is wasted and comfort is maximized.
Exploring Insulation Materials
Exploring the diverse range of insulation materials will expose you to various unique properties and costs. Some common types of insulation material include:
-
Glass wool
-
Recycled paper
-
Foam board
-
Spray foam
-
Fiberglass
-
Cellulose
Each of these materials offers different methods of protecting your home from the elements. Understanding these materials is like knowing your allies on the battlefield, each bringing a different strength to the fight for energy efficiency.
Bulk vs. Reflective Insulation
Bulk insulation, like an army of air pockets, resists heat transfer, while reflective foil insulation uses its shiny surfaces to reflect heat away from your home. Bulk and reflective insulation systems marry the two, taking advantage of both bulk material resistance and foil reflectivity, although they require careful deployment to be effective.
Innovations in Foam Insulation
Innovations in foam insulation, like Icynene and Tripolymer, are the vanguard of insulation technology, offering superior R-values and sealing capabilities that traditional materials cannot match.
Closed-cell foam, in particular, stands as a formidable barrier against moisture and air infiltration, providing an unmatched level of protection.
Eco-Friendly Options
For those who seek an alliance with the environment, blown-in insulation like cellulose and mineral wool not only offers energy savings but also brings additional benefits by maintaining consistent temperatures year-round. Structural insulated panels are another option to consider for eco-friendly insulation.
Eco-friendly cellulose is derived from plant matter, while mineral wool boasts inherent fire resistance, ensuring the safety and comfort of your home.
Installation Techniques for Maximum Efficiency
Proper insulation installation is key to preserving its protective properties. To reach maximum efficiency, it is crucial to install insulation precisely, meticulously avoiding gaps or compression and ensuring the insulation remains dry and intact. When installing insulation, following these guidelines will ensure optimal performance.
By identifying thermal bridges and sealing them, you can enhance the thermal efficiency of your home, ensuring that your insulation serves as a steadfast guardian against energy loss.
DIY vs. Professional Installation
While some homeowners may prefer DIY insulation installation, professional expertise may be needed for certain materials. Assessing your home’s energy efficiency and tackling simpler insulation tasks yourself can be cost-effective, but for complex installations, professional hands will ensure the job is done right.
Addressing Air Leakage
Air leakage is a treacherous foe that can undermine your insulation’s effectiveness. Sealing gaps during installation is as important as raising the drawbridge to protect the castle from invaders.
Spray foam, in particular, excels at creating an impenetrable barrier that also deters pests, fortifying your home against the elements and unwanted guests alike.
Ensuring Complete Coverage
Complete coverage in insulation is akin to a knight’s full suit of armor—leaving no gaps or weak points for the enemy to exploit. Insulating corners and addressing thermal bridges are critical maneuvers to prevent heat leaks and condensation, securing your home’s thermal shield.
Sealing and insulating an attic, for example, can lead to substantial energy savings, highlighting the importance of thorough insulation efforts.
Special Considerations for Insulation Projects

Insulation projects bring unique challenges and considerations. Materials such as fiberglass batts provide not only thermal resistance but also enhance the home’s safety through fire protection. Vapor barriers and pest deterrent treatments are additional considerations that can extend the lifespan and efficacy of your insulation, ensuring a secure and comfortable living environment.
Fire-Resistant Insulation Choices
Fire-resistance is a paramount quality in insulation materials, offering peace of mind alongside thermal comfort. Foam insulation and fiberglass batts are among the materials that boast fire-retardant properties, but they must be installed with precision to maintain safety standards, especially around potential heat sources.
Vapor Barrier Integration
Vapor barriers are the unsung heroes in the fight against moisture, preserving the integrity of your home’s insulation by preventing water vapor from penetrating walls and ceilings. By choosing the right materials and ensuring a tight seal, vapor barriers can effectively manage moisture levels and protect your indoor environment.
Pest Deterrence and Insulation
Insulation treated with boric acid acts as a deterrent against pests, adding an extra layer of defense to your home’s thermal barrier. The presence of pests can be an indicator of insulation weaknesses, pointing to areas where your home’s defenses may need reinforcement.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Insulation Upgrades
Investing in thermal insulation goes beyond comfort; it’s also a strategic financial move. By understanding the cost-effectiveness of increasing insulation thickness versus opting for lower thermal conductivity materials, homeowners can make informed choices that lead to significant energy cost savings.
With spray foam insulation saving up to 20% on energy costs annually, the long-term benefits can far outweigh the upfront investment.
Estimating Energy Savings
To estimate the treasure trove of energy savings your insulation can unlock, you’ll need to gather detailed consumption data before and after its installation. This process will shine a light on the expected reduction in heating and cooling loads, offering a glimpse into the potential reduction in your energy bills. Keep in mind that variables like changing weather and energy costs can influence these estimates, so it’s wise to plan for a range of outcomes.
Evaluating Long-Term Benefits
Insulation’s true value lies in its long-term benefits, which go beyond immediate energy savings to include enhanced comfort and noise reduction within your home.
By investing in the highest R-value you can afford, you are not only conserving energy but also investing in a quieter, more tranquil living space.
Payback Period Calculation
Calculating the payback period for your insulation investment is like forecasting when you’ll reap the rewards of a planted seed. By dividing the total installation cost by the annual energy savings, you can determine how many years it will take for your energy savings to cover the insulation costs, solidifying the financial viability of your decision.
Tailoring Insulation to Specific Home Areas
For optimal insulation effectiveness, you need to adapt your approach to the specific areas of your home, starting from the roof down to the foundation. Each zone has its own requirements and challenges, and addressing them with the appropriate materials and installation techniques can lead to significant improvements in your home’s energy efficiency and comfort.
Optimizing Roof and Ceiling Insulation
The roof and ceiling are the crown of your home’s thermal protection. Employing the right materials, such as batts or rigid foam boards, and ensuring proper installation can result in substantial heating and cooling cost savings.
Avoiding the compression of batts and ensuring proper barriers for loose-fill insulation are critical tactics in maintaining the fortress that is your home’s thermal barrier.
Selecting Wall Insulation
The walls of your home act as the ramparts against the elements, including radiant heat. Selecting insulation that offers high thermal resistance and acts as a radiant barrier is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor climate.
Floor Insulation Strategies
Do not overlook the ground beneath your feet—the floor is a critical battlefront in the war against heat loss. For timber floors, especially in hot climates, materials such as perforated foil can reflect heat and are best installed with precision to avoid pest infiltration.
Insulating concrete slabs or blocks can also fortify your home’s base, ensuring that every square inch contributes to your stronghold’s energy efficiency.
Summary
As we draw the curtains on this odyssey through the world of insulation, remember that the key to a well-protected home lies within the choices you make—choices informed by an understanding of R-values, tailored to your home’s unique needs, and executed with precision. Embrace the power of proper insulation and watch as your home transforms into a bastion of comfort and efficiency, ready to withstand the elements for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an R-value and why is it important?
An R-value measures insulation's ability to resist heat flow, with a higher R-value indicating better thermal performance. This is important because it directly impacts your home's energy efficiency and comfort.
Can I install insulation myself, or should I hire a professional?
It's best to hire a professional for more complex insulation types like spray foam to ensure safety and efficiency.
How do I know if my home is properly insulated?
If you notice uneven room temperatures, high energy bills, or cold drafts in your home, it may be a sign of insufficient insulation. Conducting a home energy assessment or inspecting your walls and outlets can help you evaluate the effectiveness of your insulation.
What are the long-term benefits of upgrading my home's insulation?
Upgrading your home's insulation offers long-term benefits, including reduced energy bills, improved comfort, noise reduction, and potentially increased property value.
How do I calculate the payback period for my insulation investment?
You can calculate the payback period for your insulation investment by dividing the total cost of installation by the expected annual energy savings. This will give you the number of years it will take for the savings to offset the investment cost.








